2024 - CausTiles
Category
Daylight Investigations - Region 2: Eastern Europe and the Middle East
Students
Yunus Emre Bolat & Hamza Arslan
Teacher
Furkan Sağdıç
School
Marmara University
Country
Turkey
Download
Download project board
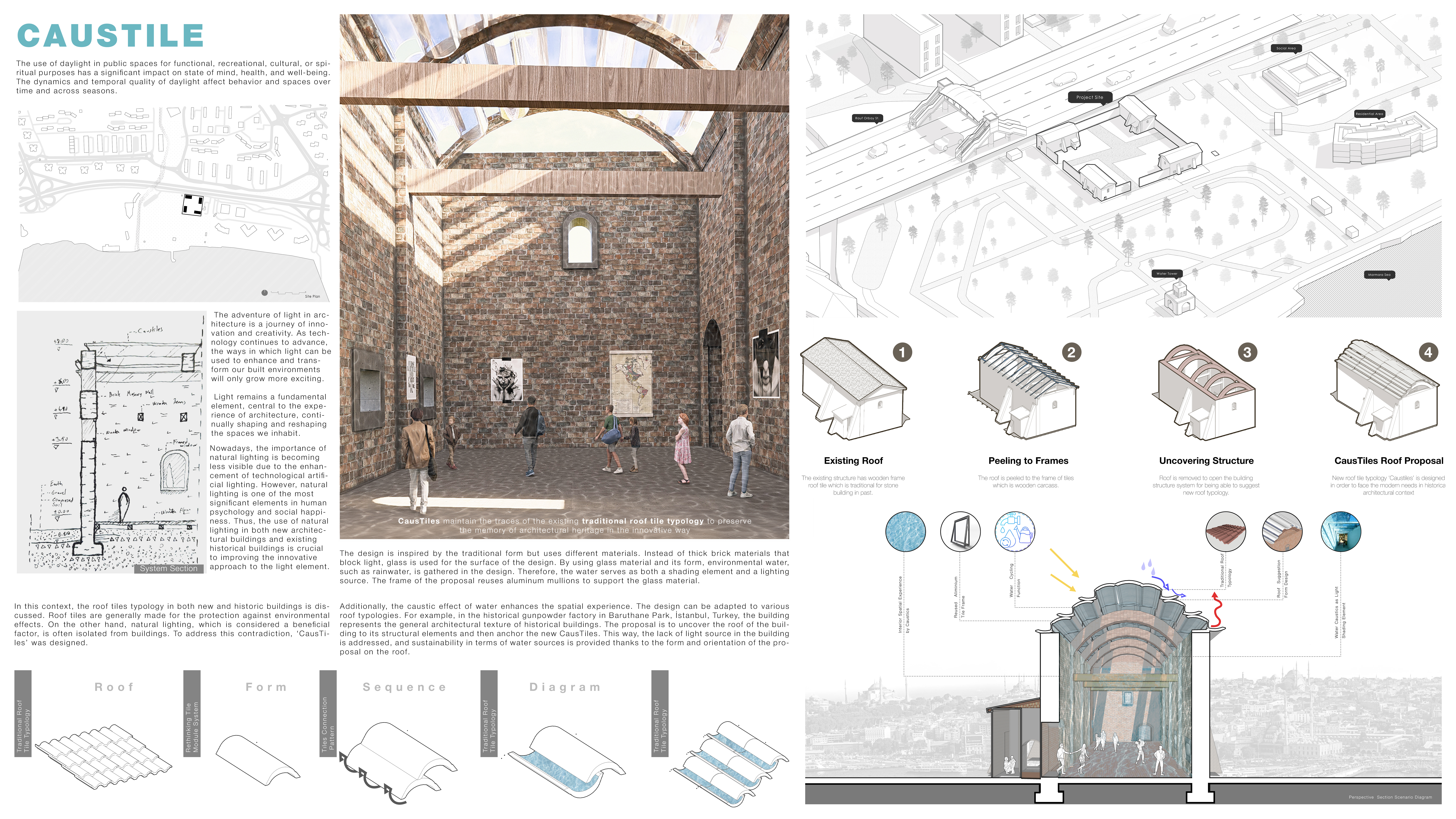
The use of daylight in public space for functional, recreational, cultural, or spiritual use and the effect of daylight on state of mind, health, and well-being as well as the dynamics and temporal quality of daylight and its effects on behavior and spaces over time and seasons.
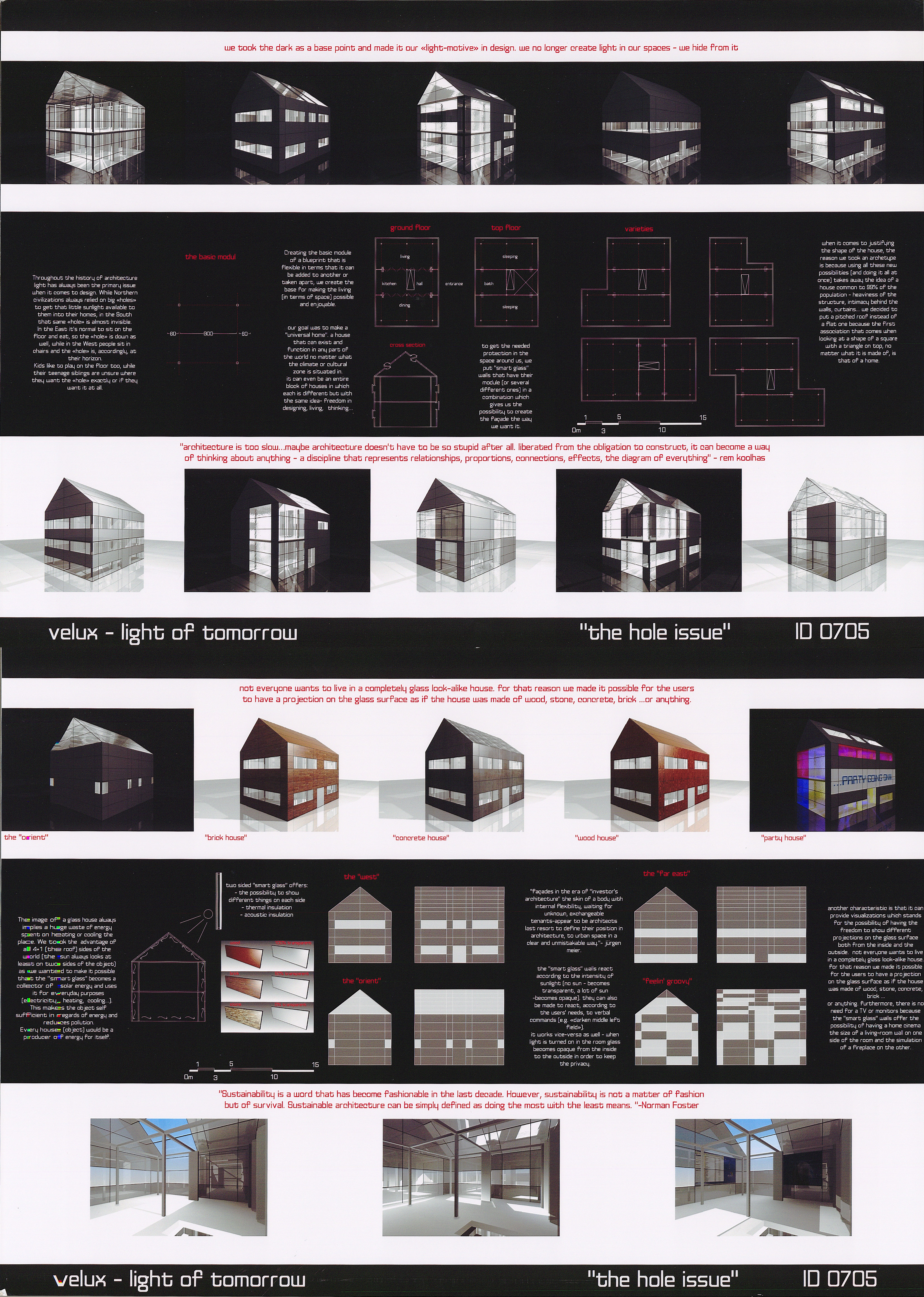
The adventure of light in architecture is a journey of innovation and creativity. As technology continues to advance, the ways in which light can be used to enhance and transform our built environments will only grow more exciting. Light remains a fundamental element, central to the experience of architecture, continually shaping and reshaping the spaces we inhabit. Nowadays, in terms of using light, the importance of natural lighting is becoming more and more invisible because of the enhancement of technological artificial lighting. However, natural lighting is one of the most significant elements in human psychology and social happiness. Thus, the use of natural lighting in both new architectural buildings and existing historical buildings is crucial to improve the innovative approach to the light element.
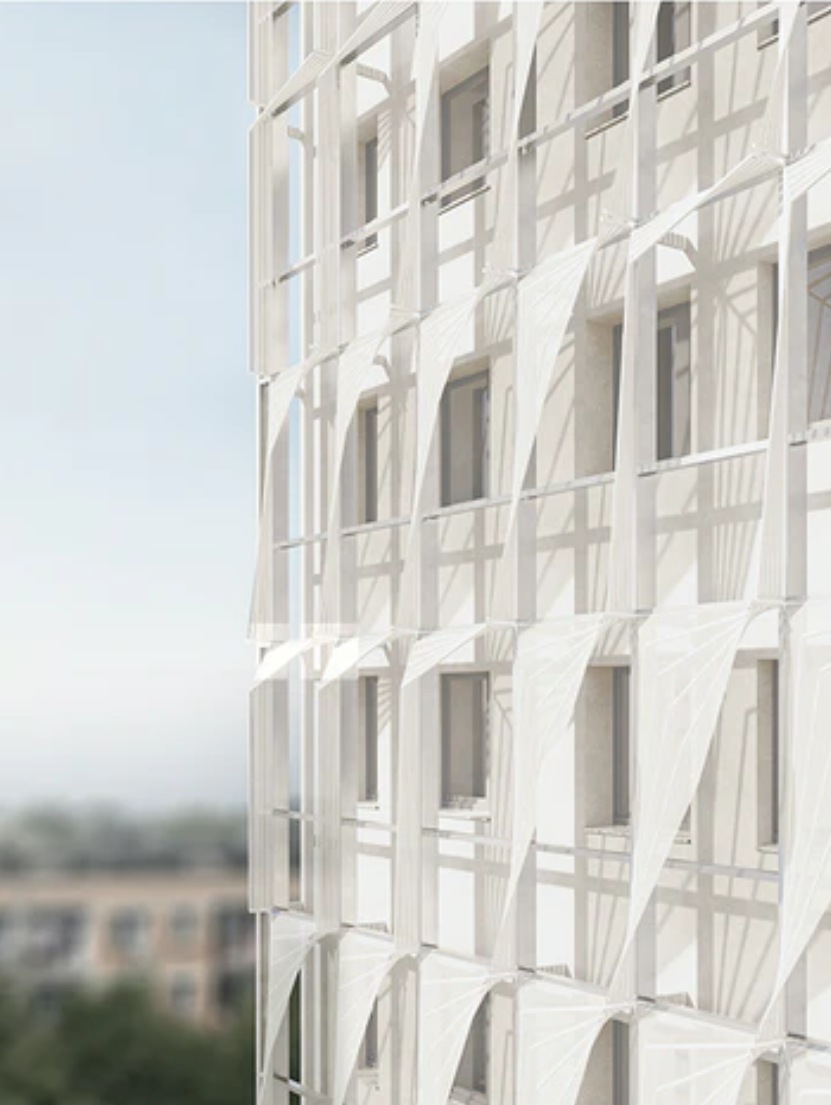
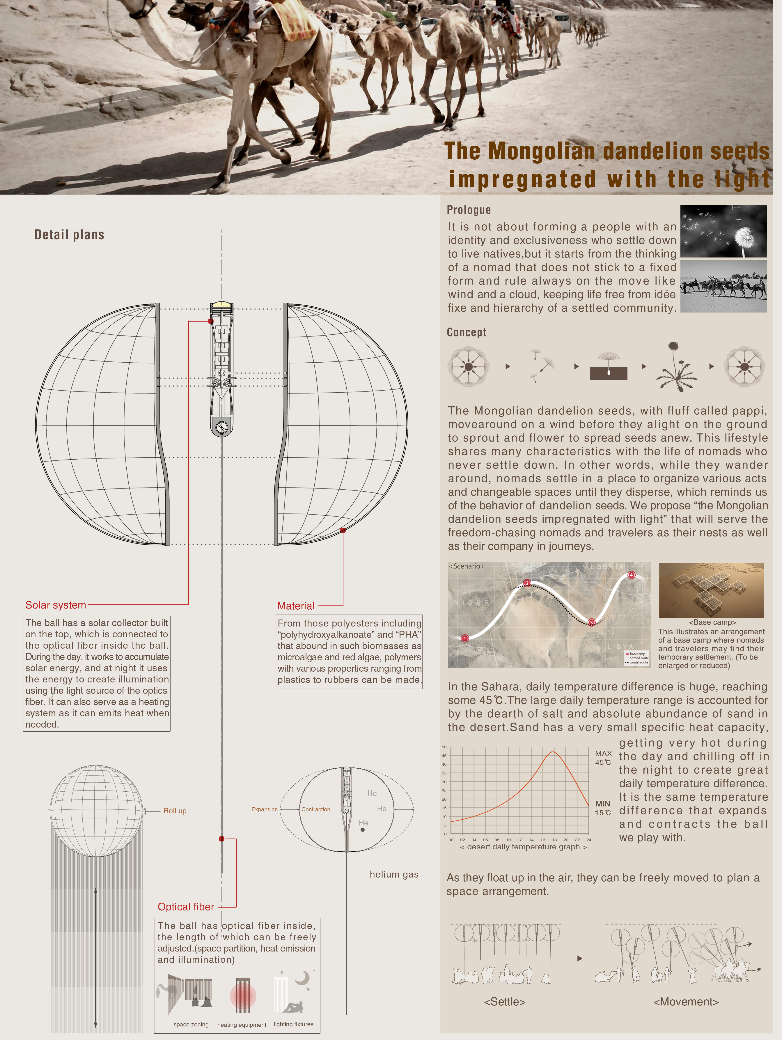
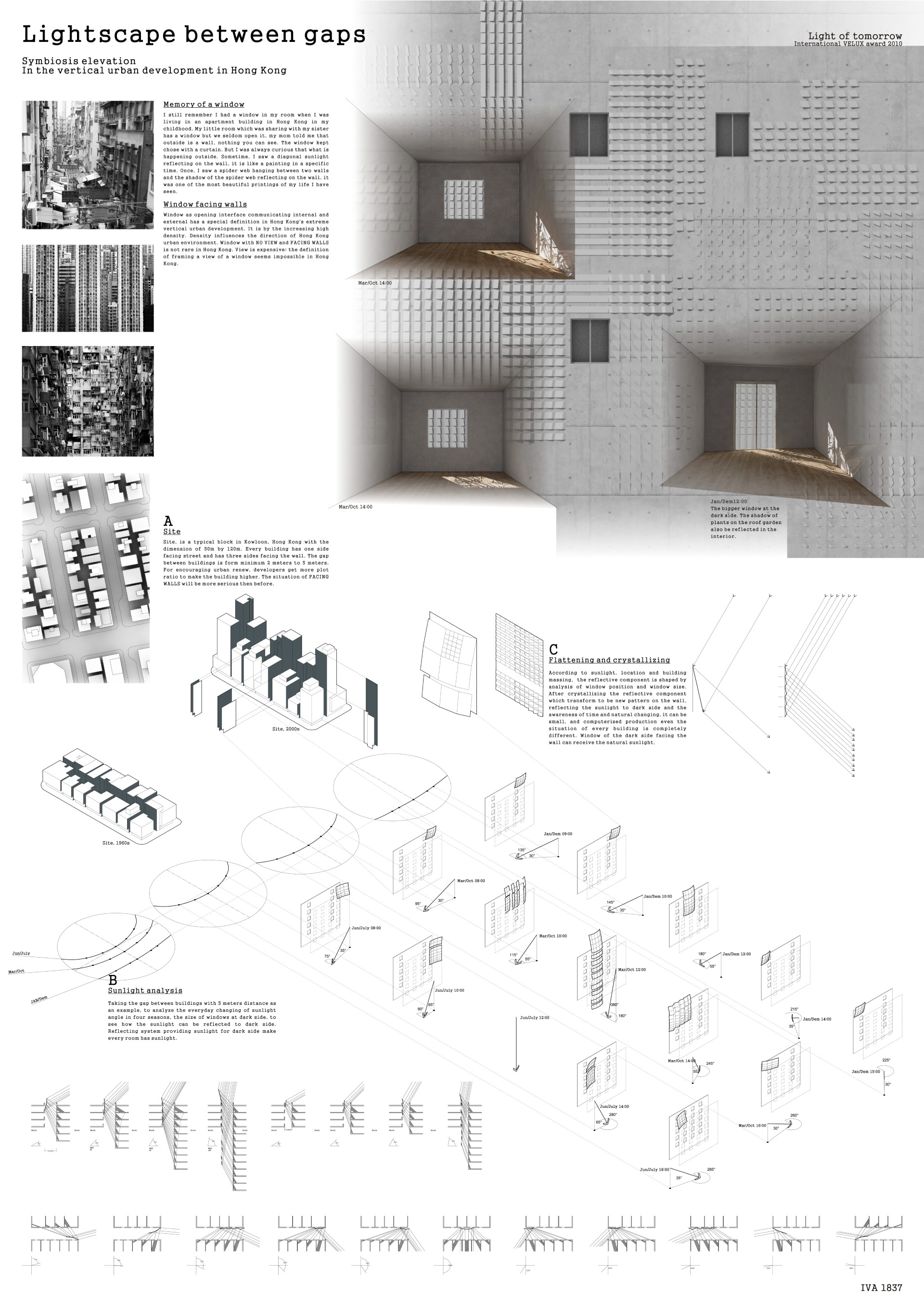
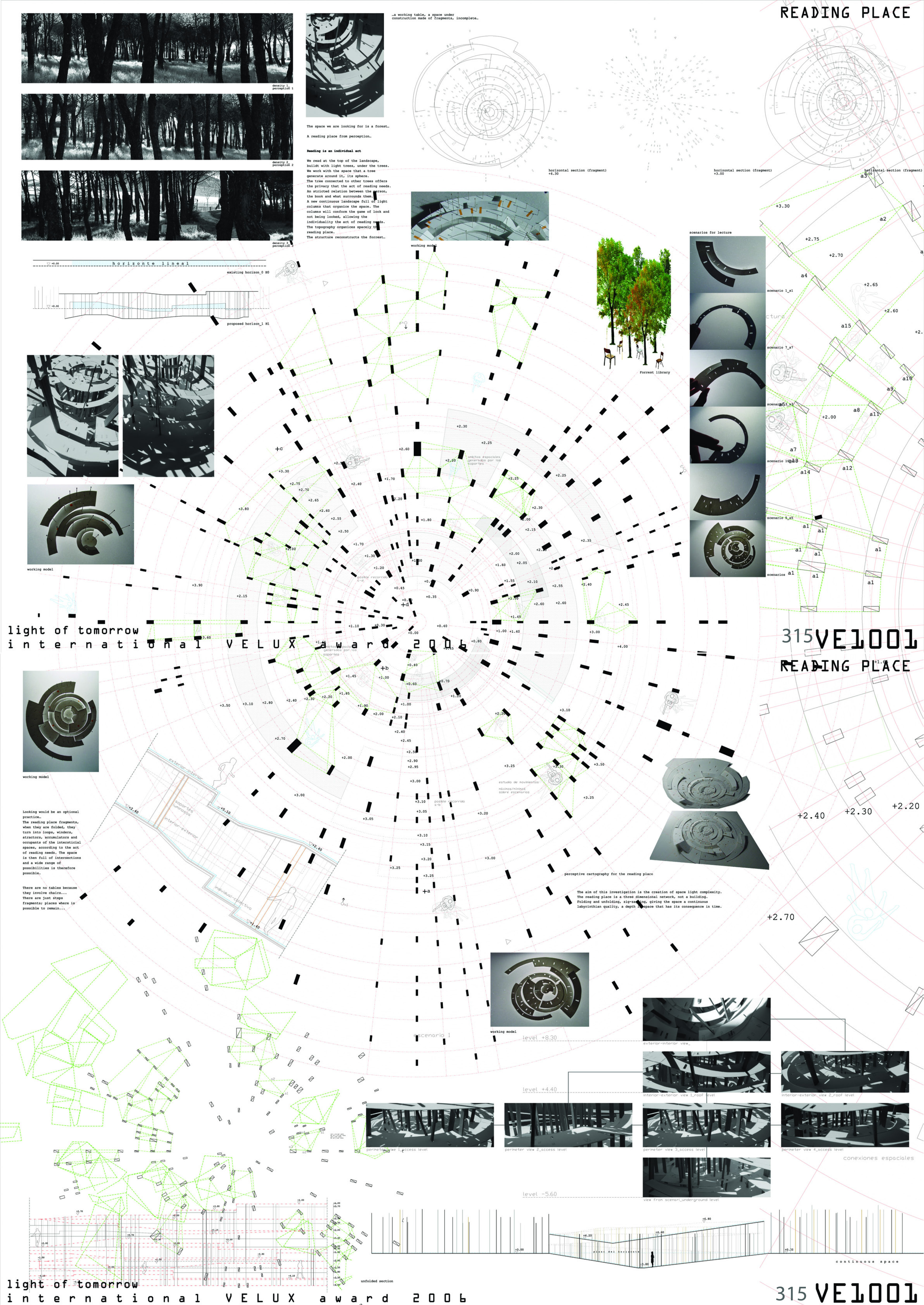
In this context, the roof tiles typology in both new and historic buildings is discussed. The tiles of the roof are generally made for the protection of environmental effects. On the other hand, the natural lighting, which is considered a beneficial factor, is also being isolated from buildings. From this point, ‘CausTiles’ was designed to solve these contradictions.
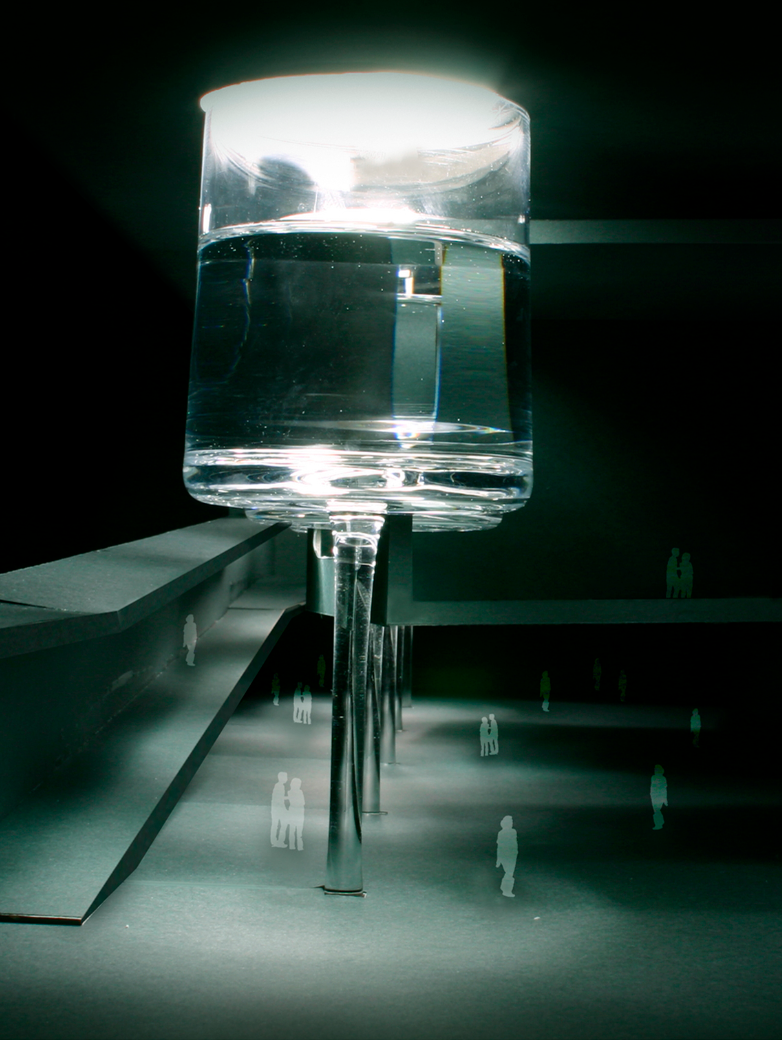
Caustiles is created with the traces of the existing traditional roof tile typology to maintain the memory of the architectural heritage. The form of the design proposal is inspired by the form of the traditional one. However, the material differs from it. Instead of using thick brick materials which prevent light, glass material is used on the surface of the design. By using glass material and its form, the water of the environment such as rainwater will be gathered in the design. Therefore, the water plays the role of both sun shading and lighting source. The frame of the proposal is reused aluminum mullions to carry the glass material.
Also, the caustics effect of water is seen as a supportive factor for the spatial experiment originating. The design can be evolved to every roof typology. In this context, the historical gunpowder factory in Baruthane Park, İstanbul/Turkey. The example represents the general architectural texture of historical buildings. The proposal is to uncover the roof of the building to its structural elements, and then anchor the new ‘CausTiles’ proposal. Doing this, the lack of a light source in the building is fixed and the sustainability in terms of water sources is provided thanks to the form and orientation of the proposal to the roof.