2024 - BORROW ME THREE HOURS MORE SUNSHINE

Category
Daylight in buildings - Region 4: Asia and Oceania
Students
Liang Zhiqing
Zhang Jiaxi
Fu Rao
Teacher
Xin Shanchao
School
Tianjin University
Country
China
Download
Download project board
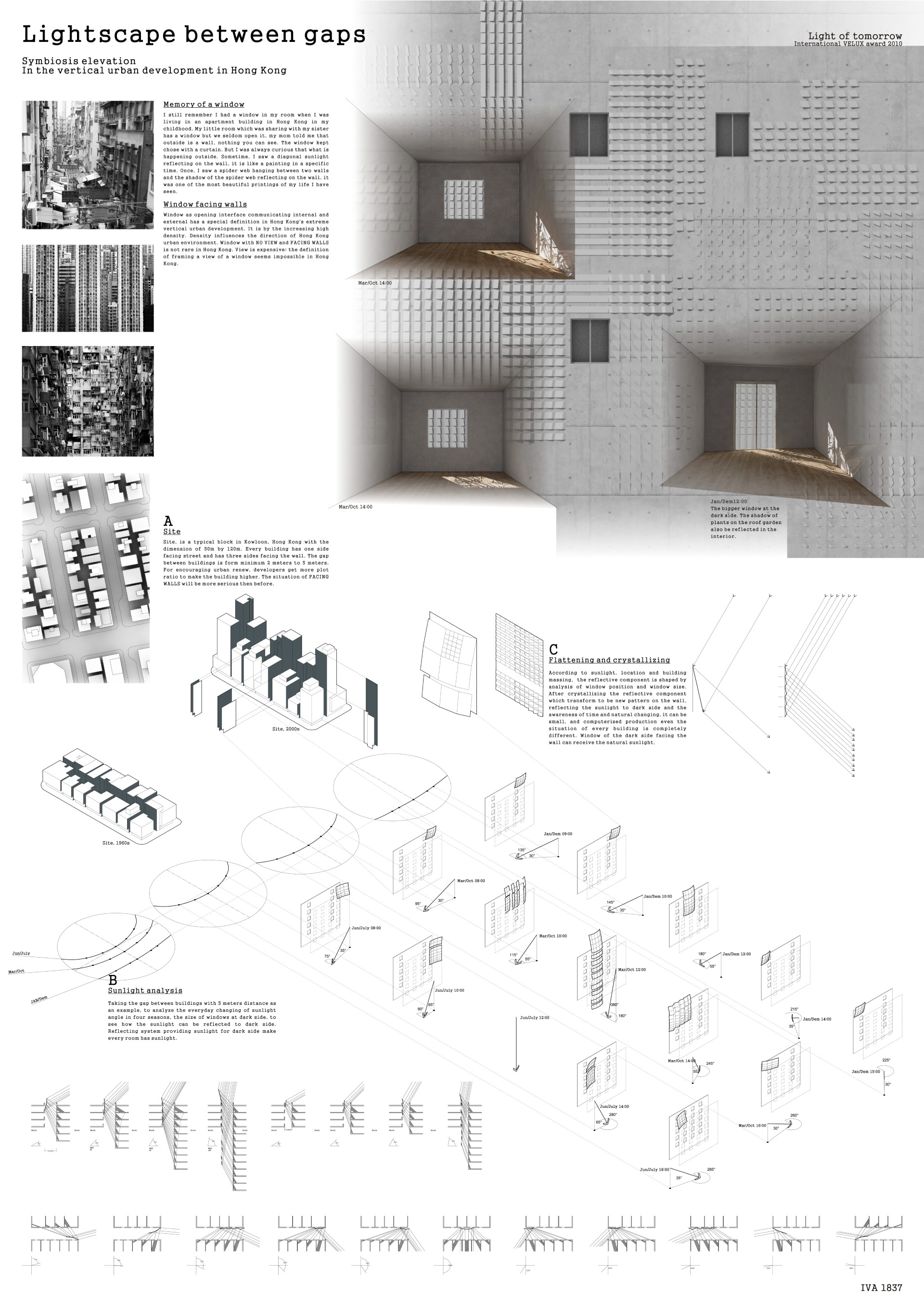
As one of China’s four super first-tier cities, Shenzhen is the first batch of key urbanization areas in China’s history. However, after the expropriation of collective land, the remaining reserved land was snatched up, and people took advantage of the urbanization boom to build residential buildings, and finally formed one after another urban villages with high building density. In the ”urban village” there is only 184,000 square meters of land, but there is a total of 441,000 square meters of floor space. The spacing of these residential buildings is extremely inconsistent with the building code (some is even less than one meter). If you stand in one building, you can even shake hands with people in the next building, so it is called the ” handshake buildings”. On this condition, the lack of sunlight becomes a serious problem.
For decades, Shenzhen, an important economic center for the country’s development, has attracted a large number of rural migrants, and these cheap rental ”handshake buildings” have become their only home in the huge super first-tier city. Tens of thousands of workers live in those narrow and depressed crevices everyday. Their physical and mental health are greatly threatened.
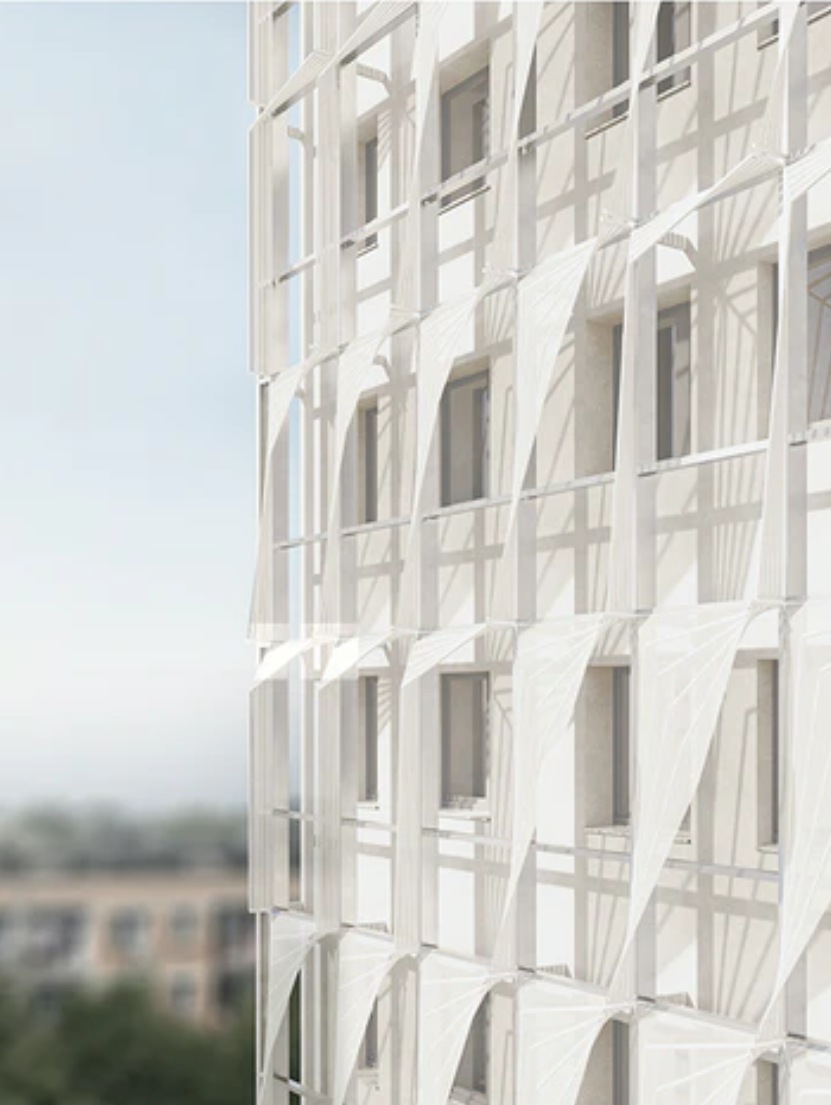
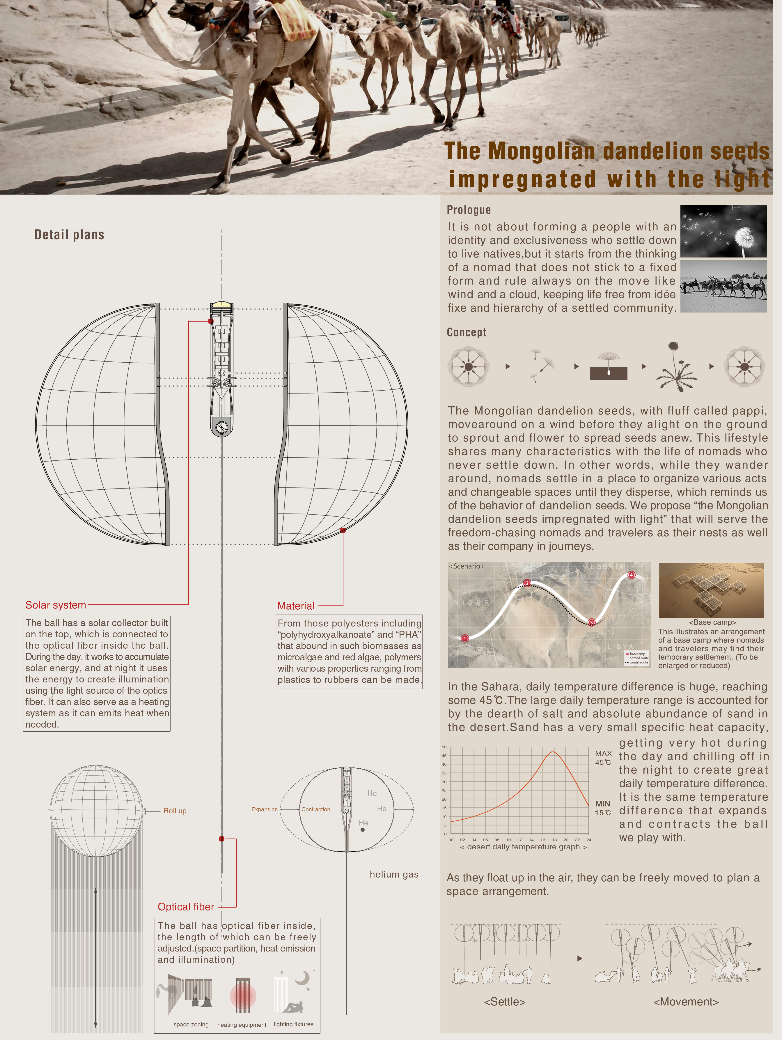
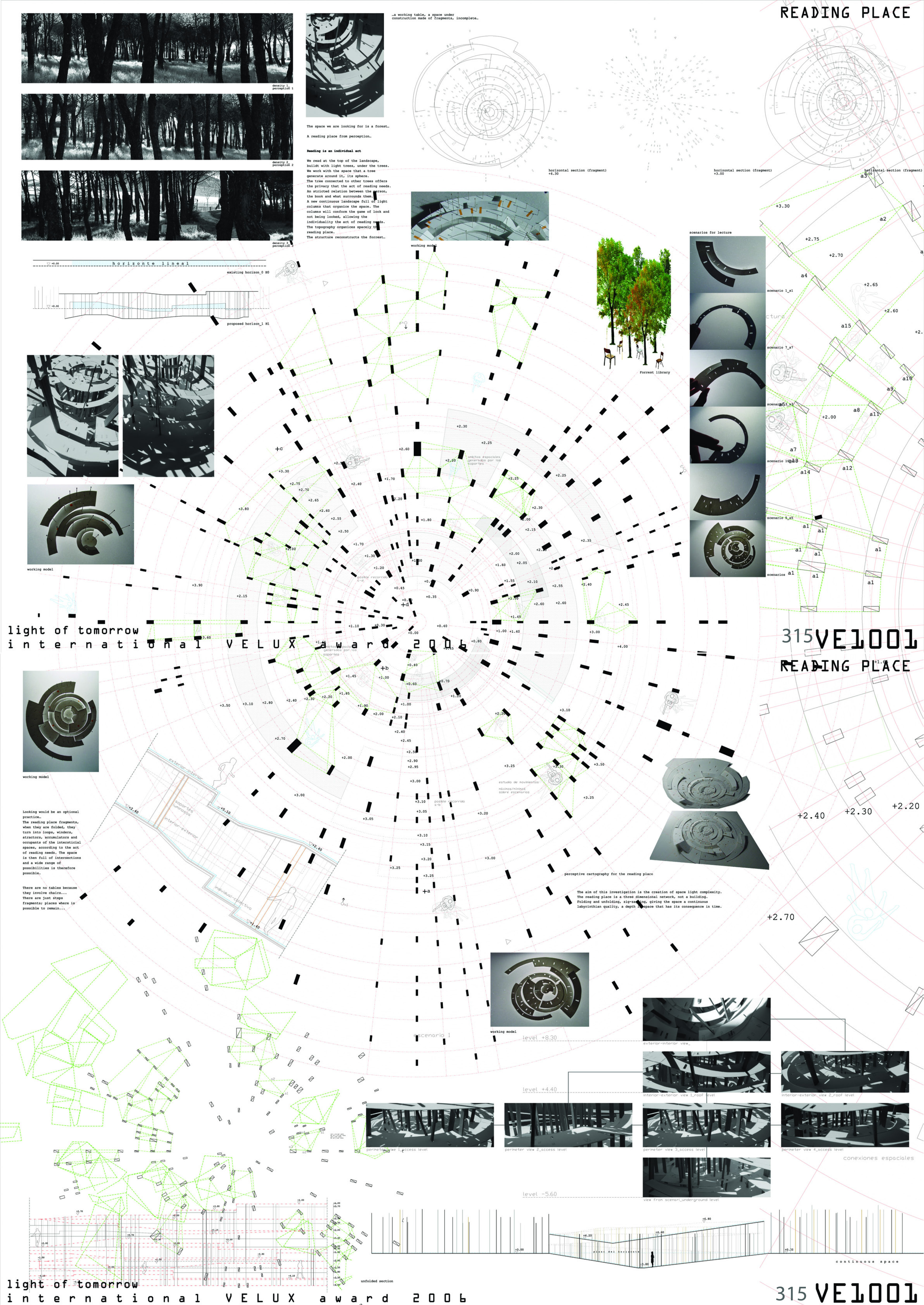
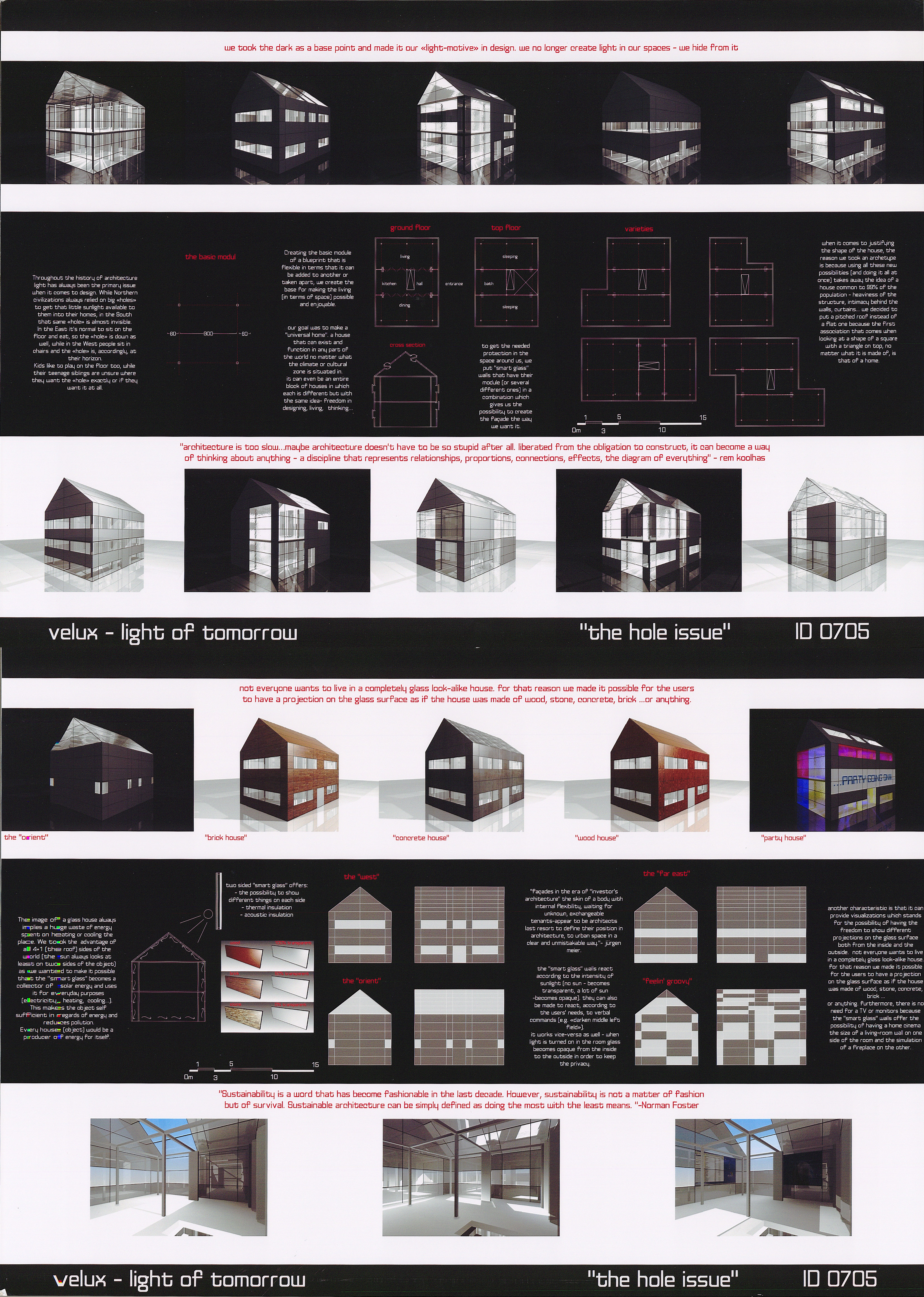
The aim of this project is to extend the sunshine time of the ”Handshake building” and expand the original sunshine range through a set of sunlight reflection devices. The device consists of two mirrors and a concave lens mounted on a glass device, positioned on the east-west edge of the roof of each ”handshake building”. The parallel sunlight shines on the first mirror on the roof, and the second mirror is established according to this reflection light, and generates an arc according to the change of the sun’s height Angle. It reflects the light for a second time, introducing the light between the buildings. The concave lens is built on the path of the second reflected light, diverting the reflected glare into a gentle light, so that the narrow gap between the ”handshake floor” has a longer time and a wider range of sunlight. While reflecting the light, under the action of the glass device on the mirror, some of the light can be scattered into a rainbow, activating the roof space and stimulating more usage of the roof space.